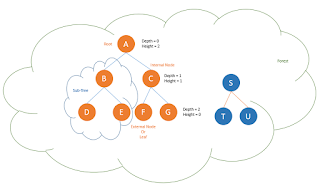
A tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure. The tree consists of nodes with a parent-child relation. The each element of the tree except the top element, has a parent and zero or more children elements.
The few applications of tree structure are Organization Data, Compiler processing, File system, Searching algorithm etc.
The node without parent is called Root.
The nodes with at least one child is called Internal nodes.
The nodes without children is called External nodes or Leaf.
The nodes which share the same parent is called Siblings.
The parent, grandparent, great-grandparent of a node is called Ancestor.
The child, grandchild, great-grandchild of a node is called Descendant.
The number of children of a node is called Degree.
The number of edges in path from root node to a node is called Depth of the node.
The number of edges in longest path from a node to a leaf is called Height of the node.
A node and its descendants in a tree is called Sub-tree.
The level of a tree is set of all nodes at the same depth. The level of Root is 0.
The set of disjoint trees are called Forest.