A function is a relation from a set of inputs to a set of possible outputs where each input is related to exactly one output.
e.g, f(x) = x2
where f - function; x - input; x2 - output
One input with many output can't be a function but many input with one output can be a function.
e.g, f(x) = x2 and f(x) = y2 can't be a function
f(x) = x2 and f(y) = x2 can be a function
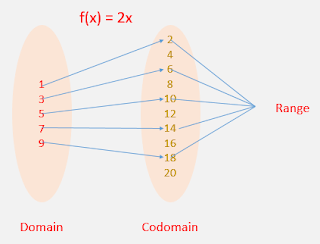
The domain is all the values that go into a function (input).
The range is all the values that come out from a function (output)
The codomain is all the possible outcome of a function.
Domain: 1,3,5,7,9
Codomain: 2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20
Range: 2,6,10,14,18
The range is a subset of the codomain.